Sizing fuses for an RV involves understanding wire sizes, circuit breakers, and the electrical demands of various appliances. Ensuring the correct fuse size is crucial for the safety and efficiency of your RV’s electrical system.
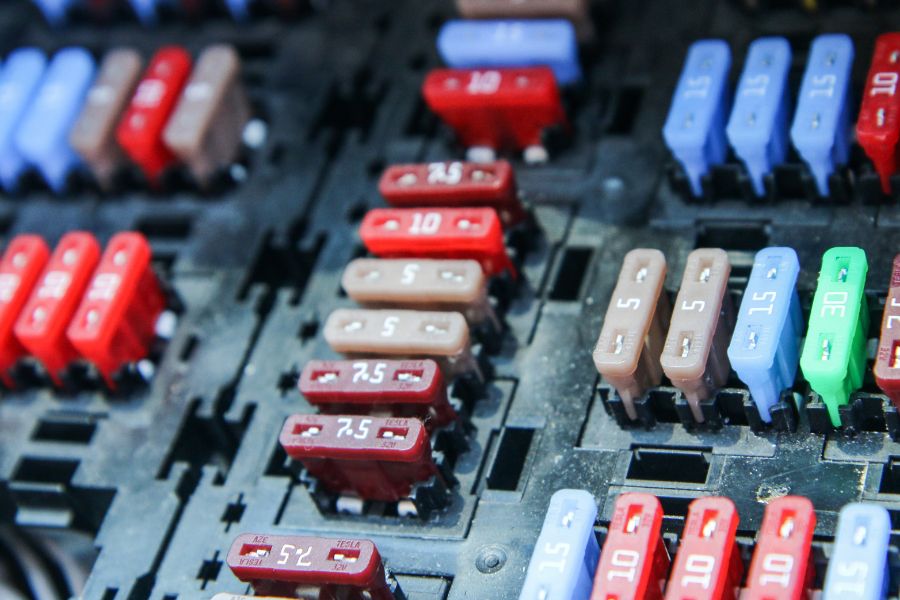
The fuse box, a central component, houses various fuse sizes, each tailored to protect specific appliances like the air conditioner, battery bank or power station. Knowing their fuse rating is essential whether you’re dealing with blade fuses or class t fuses.
Slow blow fuses, for instance, serve different purposes than standard fuses. Wiring diagrams can be invaluable tools, offering insights into the electrical flow and helping determine the appropriate fuse.
It’s also vital to consider factors like voltage drop in the DC system and the demands of shore power.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of how to size fuses for your RV, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Understanding the Role of Fuses in RVs
At the heart of an RV’s electrical system lies the fuse, a critical component designed to prevent overcurrent and potential hazards. Fuses play a pivotal role in safeguarding an RV’s electrical systems and appliances.
Their primary function is to act as a sacrificial device; when the current exceeds the fuse rating, it will blow, protecting the circuit and preventing potential damage or fires.
The fuse box, often located near the breaker box, houses various fuses, each with a specific size tailored to the wire size it protects. For instance, the air conditioner might require a different fuse size than the battery bank.
Blade fuses, class t fuses, and slow blow fuses are standard in RVs, each serving a unique purpose. Typically indicated on the fuse or in a wiring diagram, the fuse rating denotes the maximum current the fuse can handle before blowing.
Choosing the appropriate fuse size is paramount. If the size fuse selected is too high, it may not blow when needed, putting the electrical system at risk. Conversely, if it’s too low, it might blow prematurely. The goal is to find the nearest available fuse size that offers optimal protection without being overly restrictive.
Fuses are the unsung heroes of the RV electrical world, ensuring that everything from the shore power to the DC system operates safely and efficiently.
Types of Fuses Used in RVs
RVs utilize various fuses to ensure their electrical systems’ safety and efficiency. Among the most common are:
Blade Fuses
These are the most widely used in RVs, easily identifiable by their flat, blade-like connectors. They fit snugly into the fuse block and come in various sizes, each with a distinct color to indicate its fuse rating. Their compact design and clear labeling make them user-friendly.
Pros: Easy to replace, color-coded for convenience.
Cons: Removing without a proper tool can be challenging, especially in a tight fuse box.
Glass Tube Fuses
These cylindrical fuses have a glass body, allowing for easy inspection of the wire inside. They’re often used in older RV models.
Pros: Transparent design allows for easy inspection.
Cons: Fragile and can break easily.
Circuit Breakers
Unlike traditional fuses that blow and need replacement, circuit breakers simply trip and can be reset. They’re typically used for larger electrical systems, like air conditioners or the main shore power.
Pros: Reusable, eliminating the need for constant replacements.
Cons: Bulkier than a blade or glass tube fuses, and might trip unexpectedly if nearing their lifespan end.
In determining how to size fuses for an RV, it’s crucial to consider the wire size and the electrical load of the appliance. The fuse size should align closely with the system’s requirements, ensuring the nearest available fuse size is chosen for optimal protection.
Determining the Electrical Load of Your RV
Understanding the total electrical load is paramount to ensure the safety and efficiency of your RV’s electrical system. Here’s how to determine it:
- Calculate Individual Appliance Loads: List all electrical appliances and devices in your RV, from the air conditioner to smaller gadgets. Check each item’s manual or label for its wattage. If only amperage is provided, use the Watts = Amps x Volts formula. Typically, RVs operate on a 12V DC system.
- Sum Up the Wattages: Add up the wattages of all appliances to get the total electrical load. This gives you an idea of the maximum power your RV might use at any given time.
- Consider Peak Loads: Some appliances, like air conditioners, have a higher startup load. Ensure your fuse size and breaker box can handle these peak loads without tripping.
- Consult Wiring Diagrams: These diagrams, often available in your RV’s manual, provide a visual representation of the electrical system, helping you understand how appliances are interconnected and how power flows.
- Choose the Right Fuse Size: Once you know your RV’s total electrical load, you can determine the nearest available fuse size. Remember, the fuse’s primary role is to protect the wire, so ensure the wire size matches the fuse rating.
Understanding the electrical load is crucial for safety and to prevent voltage drop, ensuring all appliances function optimally. It also aids in accurate fuse sizing, safeguarding your RV’s electrical system from potential damage.
How To Size Fuses for RV
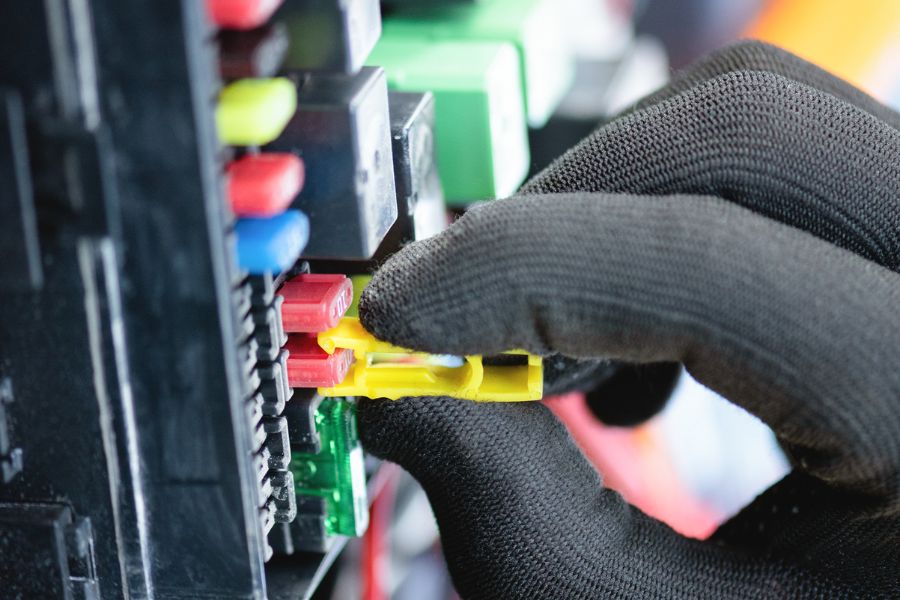

Sizing fuses for your RV is critical, ensuring the safety and efficiency of your vehicle’s electrical system. Here’s a step-by-step guide to get it right:
Calculate Correct Amperage
Begin by determining the amperage of each appliance in your RV. You can use the formula Amps = Watts/Volts if the appliance’s wattage is provided. Since most RVs operate on a 12V system, divide the wattage by 12 to get the amperage.
Consider Continuous and Starting Loads
Some appliances, like air conditioners or refrigerators, have a higher starting load (or surge load) than their continuous operating load. It’s essential to account for these peak loads when sizing fuses.
For instance, an air conditioner might typically run at ten amps but could surge up to 15 amps when starting.
Safety Margins Matter
Always add a safety margin to ensure the fuse doesn’t blow under normal operating conditions. A general rule of thumb is to add 25% to the calculated amperage. So, if an appliance draws eight amps, a 10-amp fuse (the nearest available fuse size) would be appropriate.
Choose the Right Fuse Size
Select the nearest fuse size once you’ve calculated the amperage and added a safety margin. For instance, if your calculations suggest a 13-amp fuse, you’d opt for a 15-amp fuse, a standard fuse size.
Consult the Wiring Diagram
Referring to your RV’s wiring diagram can provide insights into the electrical system’s intricacies, ensuring you place fuses in the correct locations within the fuse box.
Remember Circuit Breakers
In some RV setups, circuit breakers might be used instead of or alongside blade fuses. Ensure these are also appropriately rated for the loads they’ll handle. A circuit breaker is a different kettle of fish, but it can serve its purpose in the right conditions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Ensuring the safety and efficiency of your RV’s electrical system requires meticulous attention to detail, especially regarding fuse sizing. Here are some common mistakes to steer clear of:
Oversizing or Undersizing Fuses
One of the most frequent errors is choosing a fuse size that’s too large or too small. An oversized fuse might not blow when it should, risking damage to your appliances or wiring. Conversely, an undersized fuse can blow prematurely, even under normal operating conditions.
Ignoring Peak Loads
Appliances like air conditioners or microwaves often have higher starting or peak loads than regular operating loads. If you size a fuse based solely on the continuous load, you might find it blowing unexpectedly when the appliance starts up.
Using the Wrong Type of Fuse
Not all fuses are created equal. For instance, while blade fuses are standard in many RV applications, specific scenarios might require slow blow fuses or class T fuses. Using the wrong type can cause the fuse to blow too quickly or not when it should.
Being aware of these pitfalls and taking the time to size fuses correctly can ensure a safer and more efficient electrical system for your RV.



